Bulats Reading and Language Knowledge Pdf
Teaching Resources - Reading And Language Knowledge
- An Overview of BULATS Reading and Language Knowledge
- A detailed look at the task types with sample tasks
- DOs and DON'Ts
- Reading Skills and Strategies in BULATS
- Developing Reading Skills
- Developing Language Knowledge Skills
An Overview of BULATS Reading and Language Knowledge
The Standard Reading and Language Knowledge Test lasts about 60 minutes. Candidates should allow themselves enough time to try as much of the paper as possible, and not spend a great deal of time on a question with which they are having difficulty.
| Part | Task Focus | Number of questions |
| 1.1 | Understanding notices, messages, timetables, adverts, leaflets, graphs, etc. | 7 |
| 1.2 | Grammar and Vocabulary. Gapped sentences with multiple choice task. | 6 |
| 1.3 | Long text. Newspaper or magazine article, advert, leaflet, etc. | 6 |
| 1.4 | Grammar. Medium length text open cloze. | 5 |
| 2.1 | Reading for specific information. Four short texts with matching tasks. | 7 |
| 2.2 | Grammar and Vocabulary. Medium length text with multiple choice cloze. | 5 |
| 2.3 | Grammar. Medium length text open cloze. | 5 |
| 2.4 | Grammar and Vocabulary. Gapped sentences with multiple choice task. | 6 |
| 2.5 | Reading for gist and specific information. Long text. Newspaper or magazine article, report, etc. | 6 |
| 2.6 | Medium length text, error correction task. | 7 |
The computer test adapts to the candidate's level. If they get the question right, it will give them more difficult ones. If they got the question wrong, it will give them the easier ones. As a result, the number of questions in each section may be different from the Standard Test.
The skills tested in the Computer Test are the same as in the Standard Test.
[top]
A detailed look at the task types with sample tasks
BULATS Reading and Language Knowledge – Task Type 1 – Multiple Choice – notices, leaflets, graphs etc.
(Found in Part 1 Section 1)
Task Description
What sort of material do candidates read?
� Very short business-related texts, or simple graphics.
� Each one could be found in a business context.
� The main purpose of each is to provide information.
� Questions cover Levels 1 to 4.
What do the candidates have to do?
There are 7 multiple choice questions, one on each text. For each question, candidates have to choose one of the three options (A-C).
What skill is being assessed?
Understanding of short, real-world notices, messages, leaflets, newsflashes, adverts and graphics, and identification or interpretation of their meaning.
Understanding the Task
To understand better how candidates need to approach this task, it may help you to do the activity yourself and analyse what you had to do to find the right answer. Look at this sample Task Type 1 task from a past BULATS Reading and Language Knowledge paper. Complete the task, thinking about how you are doing it.
Sample Task Type 1 Task
Sample
Look at the two questions below. Complete the task, thinking about how you are doing it.
1 (This is at about Level 2.)
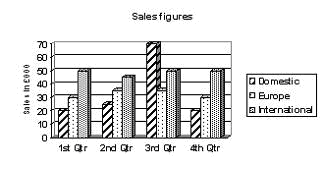
| A | International sales remained fairly constant throughout the year. |
| B | Sales within |
| C | Domestic sales collapsed in the second quarter of the year. |
2 (This is at about Level 3.)
Jardine's has overhauled packaging across its 40-strong breakfast cereal, fruit bar and snack bar portfolio in an effort to create a single and more recognisable brand identity.
Jardine's has changed its packaging so that consumers can more easily
| A | distinguish between different Jardine ranges. |
| B | pick out Jardine's products. |
| C | decide which Jardine product suits them best. |
Answers
1.A
2.B
Things to consider
Now look at these questions about how you approached the task and consider your answers.
1. Did you read the question and options first, or look at the input (the text or graphic)?
2. Did you consider all three options before choosing the answer?
3. Did you read the whole of the text before finalising your answer?
4. Did the options repeat words exactly as they are found in the texts?
BULATS
(Found in Part 1 Section 2 and Part 2 Section 4)
Task Description
What sort of material do candidates read?
� Separate business-related sentences.
� Part 1 Section 2 covers Levels 1-3.
� Part 2 Section 4 covers Levels 3-5.
What do the candidates have to do?
There are 6 multiple choice questions in each Part. Each one consists of a sentence with a gap, and four options. For each question, candidates have to choose one of the 4 options (A-D).
What skill is being assessed?
Knowledge of grammar and vocabulary.
Understanding the Task
To understand better how candidates need to approach this task, it may help you to do the activity yourself and analyse what you had to do to find the right answer.
Look at this sample Task Type 2 task from a past BULATS Reading and Language Knowledge paper. Complete the task, thinking about how you are doing it.
[top]
DOs and DON'Ts
Do's
- Make sure you understand the instructions for each task, and follow them exactly.
- Try to answer all the questions – you won't lose marks for wrong answers, and there's a chance that you'll guess correctly.
- Carefully copy your answers in pencil onto the Answer Sheet.
- If a question or part looks difficult, leave it, go on to something else, and come back to it later.
- Leave yourself enough time to check your answers, and to check that you've copied them correctly onto the Answer Sheet.
- Concentrate on understanding the main points of a text, rather than every single word.
- Remember that the texts range from a low to a high level of English, so you aren't expected to understand everything.
Don'ts
- Don't leave any answers blank.
- Don't spend too long thinking about a question.
- Don't worry if you find a text difficult to understand.
Don't try to understand every single word in a text.
[top]
Reading Skills and Strategies in BULATS
How do we read texts?
We use different approaches to read different texts. We can read quickly or slowly, skimming for the general ideas or scanning for a specific point. How we read depends on the text - its length, its type - and our purpose in reading it - for information, for the general idea, etc.
In the BULATS Reading and Language Knowledge paper, candidates need to identify the text type and the purpose of the task and to apply the appropriate approach.
Our relative success as readers is shown in the outcome of our reading. Do we find the information we want, or understand the general idea? Succeess depends on applying different reading strategies to different types of text.
The range of tasks and text types in the BULATS Reading paper requires candidates to apply these different strategies effectively.
Here are some situations in which you would apply different approaches to reading:
- When you look through your in-tray to decide how to prioritise your work, you read for gist .
- When you look at the front page of the newspaper on the bus but you only have a few minutes before your stop, you read for the main points .
- When you read an instruction manual on how to mend the photocopier, you read for detailed understanding .
- When you look at two product brochures to decide on a particular supplier, you read for specific information .
- When you look at a sign in a language you don't know, you have to deduce the meaning .
- When you check a piece of business correspondence or a report you have written, you edit your work .
[top]
Developing Reading Skills
- Making use of clues - learners should be able to use the titles, illustrations and the look of the text (bold, italics, paragraphing etc.) to decide what kind of text it is and to start making a few general predictions about its content. The strategy of predicting is very useful.
- Understanding gist - this is the ability to form a general overview of a text from just making use of the clues and a very quick reading. This means that learners should be skimming texts.
- Understanding relevant details - learners will be looking for the details that are relevant to the writer's reason for writing, the subject matter of the text and the reader's purpose for reading. For example, if someone is looking at a timetable of all the trains that leave from a particular station, the relevant information are just the details of the journey the reader wishes to take. This is called scanning .
- Distinguishing main points from secondary points - knowing how a paragraph is structured and how the main point is often made first and then supported by less important detail could help a learner find the information they need. Interpreting is a key strategy here.
- Distinguishing fact from comment - being able to find the comment will help with understanding the writer's opinions and attitudes and means the reader needs to interpret the text.
- Identifying relevant information - this is often done by stopping to think about the text and discussing the intended audience, the writer's attitudes and opinions, and the inferences that can be drawn from explicit information in the text. Again, interpreting is important here.
- Deriving meaning from texts that contain unknown words and phrases - this requires the learner to be able to guess meaning from context or ignore a word they don't know. This is a coping strategy.
- Using appropriate aids - reference books should be available and learners need to know how to use dictionaries and grammars etc. These will support their learning even if there is no teacher around and help the learner be more independent. Again, this is coping with difficulties and problems when learning.
[top]
Developing Language Knowledge Skills
A number of sections of the BULATS test deal with knowledge of grammar and vocabulary. The sections below give advice on how to work on these areas.
Integrate with skills work
Skills such as recognising cohesion in texts, understanding the grammatical and logical connection between words and between different parts of a piece of writing, proofreading and error correction will form an important part of students' language learning. The texts and tasks reflect real-life skills and approaches to language learning.
Encouraging students to read newspapers, magazines, brochures, notices, advertisements, emails, notes, reports, memos, etc. both inside and outside the classroom will help them acquire more vocabulary and fluency and should improve their performance on all parts of the BULATS exam. Stimulating students to make use of the internet, emails and of the increased presence of English all around them (television, films, labels, instruction manuals, brochures etc.) as sources of different types of English and different types of text will have a positive effect on their language.
Vary the focus of reading by spending time in class looking at cohesion and coherence in written texts.
Work on vocabulary which appears in reading and listening activities, with a focus on form, meaning and collocation, as well as regular practice with word building, will help build important language-learning skills.
When dealing with students' written work, encourage them to check their own and each other's work and use their errors for error-correction practice.
In these ways, integrating activities for the RLK paper into general skills work inside and outside the classroom is both easy and beneficial.
Focus on grammatical form, vocabulary and spelling
Do not neglect work on grammatical form, vocabulary and spelling. Regular practice will stimulate students and help them remember new language and extend their knowledge.
Trying to stimulate students so that a greater awareness of and interest in these areas are developed outside the classroom will be of enormous benefit. A great deal of computer software and internet material is targeted at these specific areas of language and students should be encouraged to make use of this both in class and outside, either on their own or together with friends.
Show students what is involved
By examining the best approach to each task and by asking students to create their own tasks, teachers can improve their performance on this and the other BULATS papers.
How to stimulate interest in students
You should vary the length of your activities. For example, sometimes you can use a word building exercise as a quick warmer to start the class.
Error correction can also be varied by giving them ten sentences and telling them to find mistakes in five.
Don't forget to praise as well as criticise! Tell your students the things they have done well. If students use an expression that they have been studying recently in their written work or when they are speaking, point it out and congratulate them.
Explain that probably the only way that they can make tangible progress is by trying out new words and expressions so that they become part of their repertoire.
Put your students in situations where they have to try out their language and where they can perceive the need to learn more. Often, they can 'get by' in most familiar situations but when faced with an unfamiliar context they will see that they need to acquire more resources.
[top]
Bulats Reading and Language Knowledge Pdf
Source: https://www.bulats.com.my/teaching_resources_-_reading_and_language_knowledge.html